Lessons from complex networks to smart cities on Nature Cities
Interesting review article on Nature Cities by ISC Director Guido Caldarelli
Abstract
A smart city is an urban area that uses technology, data and digital infrastructure to improve the quality of life for its citizens, enhance the efficiency of city services and promote sustainability. Complex networks can enable the extraction of useful information from technologies, such as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence and big data analytics, in a comprehensive way. This would enable common urban challenges, such as traffic congestion, pollution, waste management and energy usage, to be addressed. Network theory offers a strong framework for analyzing and visualizing complex relationships in urban environments, including transportation, social interactions and infrastructure. This interdisciplinary approach aids in comprehensive city modeling and serves as a vital tool for policymakers to improve the robustness and resilience of urban landscapes.
Per saperne di più leggi anche La Scienza delle reti può guidare le città verso un futuro davvero smart.
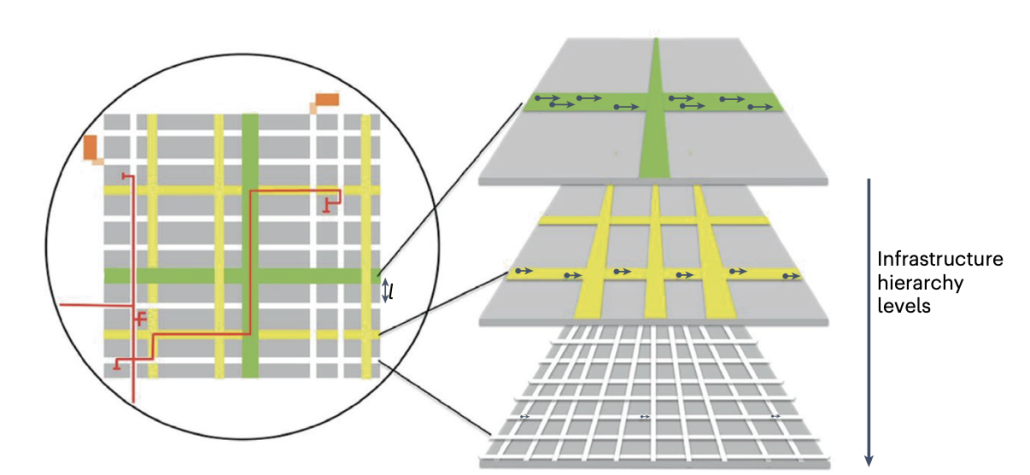
Mechanisms for urban growth and transformation – Social and dissipative processes shape the structural growth.
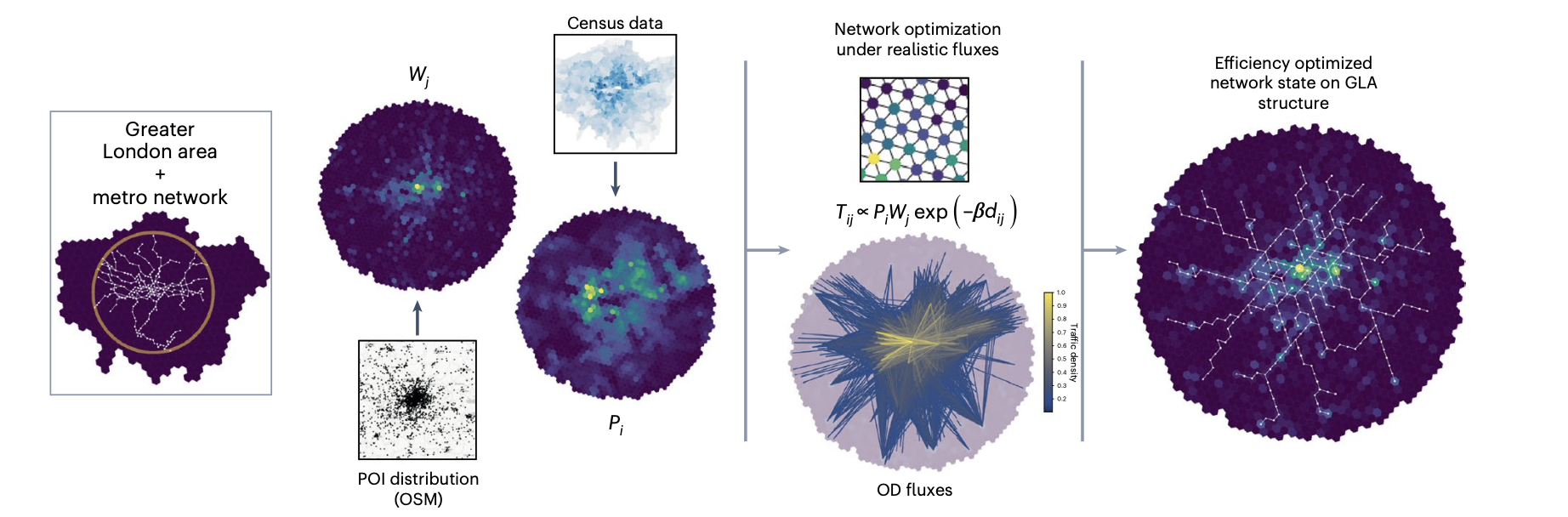
A maximum-entropy model that optimizes flow efficiency in the Greater London area (GLA): a central core and peripheral branches with loops, as observed in the empirical metro network, spontaneously appear45. Tij, spatial interaction flows between nodes i and j; dij, distance between nodes i and j; Wj, attractiveness of node j; Pi, population density of node i; OD, origin–destination; POI, point of interest; OSM, Open Street Map.