Frontiers in Cell Biology: Rescue of Alpha-Synuclein Deficit by Virus-Driven Expression or by Running Restores the Defective Neurogenesis
ISC researcher R. Coccurello coauthored an interesting article now published in Frontiers in Cell and developmental biology
L. Micheli, T. Creanza, M. Ceccarelli, G. D’Andrea, G. Giacovazzo, N. Ancona, R. Coccurello, R. Scardiglli, F. Tirone, Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 17 August 2021
The dentate gyrus of the hippocampus and the subventricular zone are neurogenic niches where neural stem and progenitor cells replicate throughout life to generate new neurons. The Btg1 gene maintains the stem cells of the neurogenic niches in quiescence. The deletion of Btg1 leads to an early transient increase of stem/progenitor cells division, followed, however, by a decrease during adulthood of their proliferative capability, accompanied by apoptosis. Since a physiological decrease of neurogenesis occurs during aging, the Btg1 knockout mouse may represent a model of neural aging. We have previously observed that the defective neurogenesis of the Btg1 knockout model is rescued by the powerful neurogenic stimulus of physical exercise (running). To identify genes responsible for stem and progenitor cells maintenance, we sought here to find genes underlying this premature neural aging, and whose deregulated expression could be rescued by running. Through RNA sequencing we analyzed the transcriptomic profiles of the dentate gyrus isolated from Btg1 wild-type or Btg1 knockout adult (2-month-old) mice submitted to physical exercise or sedentary. In Btg1 knockout mice, 545 genes were deregulated, relative to wild-type, while 2081 genes were deregulated by running. We identified 42 genes whose expression was not only down-regulated in the dentate gyrus of Btg1 knockout, but was also counter-regulated to control levels by running in Btg1 knockout mice, vs. sedentary. Among these 42 counter-regulated genes, alpha-synuclein (Snca), Fos, Arc and Npas4 showed significantly greater differential regulation. These genes control neural proliferation, apoptosis, plasticity and memory and are involved in aging. In particular, Snca expression decreases during aging. We tested, therefore, whether an Snca-expressing lentivirus, by rescuing the defective Snca levels in the dentate gyrus of Btg1 knockout mice, could also reverse the aging phenotype, in particular the defective neurogenesis. We found that the exogenous expression of Snca reversed the Btg1 knockout-dependent decrease of stem cell proliferation as well as the increase of progenitor cell apoptosis. This indicates that Snca has a functional role in the process of neural aging observed in this model, and also suggests that Snca acts as a positive regulator of stem cell maintenance.
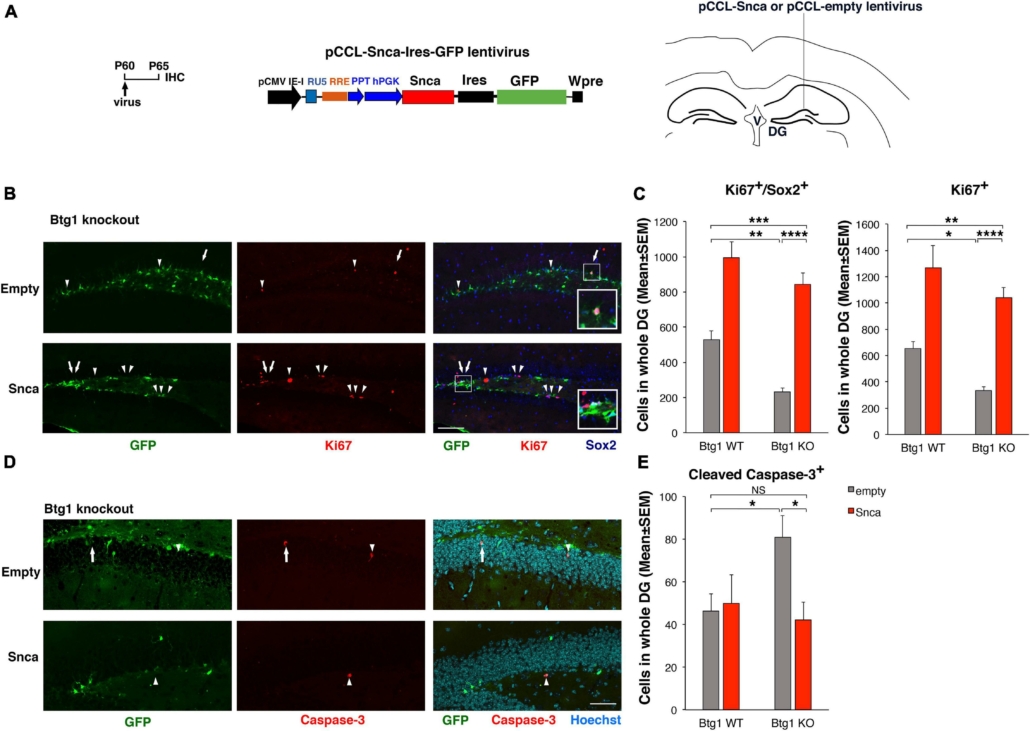
Rescue of the defective alpha-synuclein expression in Btg1 knockout dentate gyrus through virus-mediated transfer reactivates stem cell proliferation and reverses the increased apoptosis. (A) Lentivirus infection protocol, structure and injection area of the virus. DG, dentate gyrus; V, ventricle. (B) Representative confocal images (20 × magnification) of coronal sections of the dentate gyrus of Btg1 knockout mice, labeled with Ki67, Sox2 and GFP (in red, blue and green, respectively), 5 days after infection with either pCCL-Snca or pCCL-empty lentiviruses. The white arrows indicate triple-labeled cells for GFP, Ki67, and Sox2; white arrowheads indicate cells labeled for Ki67. The white box area is shown with 2.4 × digital magnification. Scale bars, 100 μm. (C) Quantification of the absolute number of proliferating dentate gyrus stem cells (type-1-2a; Ki67+/Sox2+) and of total proliferating progenitor cells (Ki67+). The significant decrease of Btg1 KO stem cells (infected with empty virus), relative to Btg1 WT, is reversed above control levels in KO mice infected with pCCL-Snca virus (Analysis of simple effects: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; or ****p < 0.0001, Fisher’s PLSD ANOVA post hoc test). (D) Representative images by confocal microscopy (40 × magnification) of apoptotic cells in the dentate gyrus of Btg1 knockout mice, labeled with activated Caspase-3 (in red) and GFP (in green), 5 days after infection with either GFP-Snca or GFP-empty lentiviruses. Nuclei are counterstained with Hoechst 33258 (cyan). The white arrow indicates a cell double positive for GFP and activated Caspase-3 and the white arrow heads indicate cells positive for Caspase-3. Scale bars, 50 μm. (E) Quantification of the absolute number of apoptotic stem cells (Caspase-3+). The increase of apoptosis observed in Btg1 KO dentate gyrus, relative to Btg1 WT, infected with empty lentivirus is reversed by infection with lentivirus overexpressing GFP-Snca. *p < 0.05; NS p > 0.05; Mann-Whitney, U-test. Cell numbers in the dentate gyrus in panels (C,E) are means ± SEM of the analysis of four animals per group.


